What Is the Primary Stimulus for Ventilation
What is the primary chemical stimulus for changes in ventilation. During moderate exercise ventilation increases in the exact proportion to VCO 2.

What Is The Primary Stimulus For Breathing
See answer 1 Best Answer.

. Which of the following statements are true of the dorsal respiratory group DRG. It consists mainly of inspiratory neurons. Alveolar P CO2 P ACO2 depends on the balance between the amount of CO 2 being added by pulmonary blood and the amount being eliminated by alveolar ventilation V A.
Level of CO2 in the body C. What is the most important stimulus in the control of ventilation. Oxygen is critical for proper metabolism.
What is the primary stimulus to breathe in human beings without pulmonary diseases. It helps bring oxygen to the blood and remove carbon dioxide from the body. What effect will a complete injury above C3-C5 have on a patients spontaneous ventilation.
Breathing is a complex process that relies heavily on the coordinated action of the muscles of respiration and the control center in the brain. Such as chemoreceptor stimulus and hypothalamus stress response. Respiration is the exchange of gases between the lungs and pulmonary blood vessels external respiration and between the blood and tissues internal respiration.
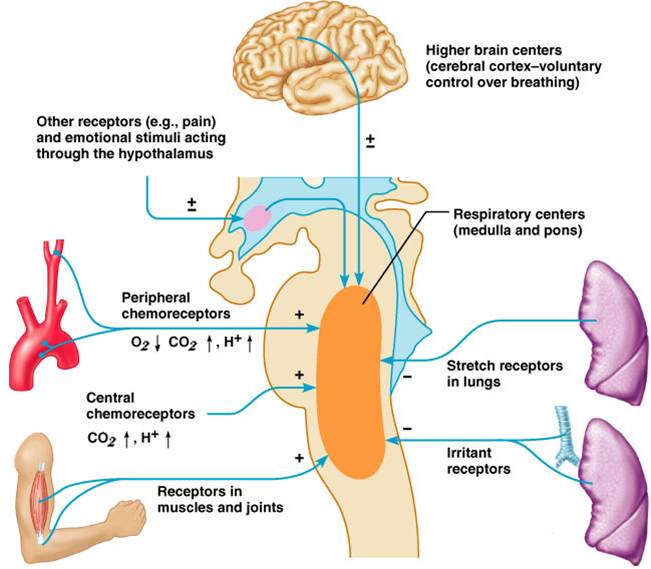
-Send signal via vagus nerve to respiratory center in medulla to end inspiration. Its main function is to send signals to the muscles that control respiration to cause breathing to occur. This system though slower than the peripheral chemoreceptors is the primary stimulus of ventilation and is estimated to provide 80 of the stimulus for a ventilatory response to a raised arterial CO 2.
Amount of nitrogen in air. These neurons are involved in the hering breuer and heads. Is the primary stimulant for ventilation in healthy persons while hypoxia.
During very short-term bouts of intense exercise the release of lactic acid into the blood by the exercising muscles causes a fall in the blood plasma pH independently of the rise in the PCO2 and this will stimulate pulmonary ventilation sufficiently to keep the blood pH constant at the expense of a lowered PCO2. This is an important point to remember as it is not unusual for patients on. At a pH of 73 and a CO2 of 40 as the Pco2 increases the alveolar ventilation increases.
During submaximal steady-state exercise increases in ventilation are proportional to the increase in carbon dioxide production V co 2 and oxygen consumption V o 2. Amount of oxygen required by the body B. The phrenic nerves vagus nerves and posterior thoracic nerves are the major nerves involved in.
It sends impulses to the phrenic and external intercostal motor in the spinal cord. However despite the long. What is the most powerful stimulus of the medullary respiratory centers.
The most important stimulus for regulation of ventilation in healthy persons is increased levels of carbon dioxide. 2012-11-01 22. Click card to see definition.
-Stretch receptors in located in the walls of the bronchi and bronchioles and in the visceral pleura keep lungs from overinflating -Stimulated when lungs hyperinflate. Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract Receptors Important receptors in the lung and the upper respiratory tract provide afferent information to the respiratory centers. Oxygen and carbon dioxide move from one area to the other due to pressure gradients.
The diffusion of gases brings the partial pressures of O 2 and CO 2 in blood and alveolar gas to an equilibrium at the pulmonary blood-gas barrier. The medulla oblongata is the primary respiratory control center. Explain the strategic significance of the location of the peripheral chemoreceptors.
At the lower pH and. Level of oxygen in the body D. What chemical signals activate the carotid and aortic bodies.
At a pH of 74 a higher CO2 is required to drive an increase in alveolar minute volume. The increase does not occur because of changes in PO 2 PCO 2 and H. The body is truing to blow off CO2.
Hypoxia and hypercapnia interact at the level of the carotid body and their combination is an extremely powerful stimulus to ventilation. During exercise ventilation may increase 20 times. Ventilation is the movement of air between the lungs and the surrounding environment.
The primary function of the lungs is to facilitate gas exchange between inspired air and the circulatory system. As such this tight regulation of ventilation to metabolic rate ensures the homeostasis of the arterial partial pressure of oxygen P a O 2 carbon dioxide P a CO 2 and pH. The major stimuli to ventilation during exercise remain unclear.
Hering - Breuer Reflex. Complete diaphragmatic paralysis would result- patient would require mechanical ventilation. As the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in arterial blood rises ventilation increases nearly linearly.
Carbon dioxide is one of the most powerful stimulants of breathing. It provides the main stimulus for inspiration. P A CO 2 P a CO 2 and P A CO 2 VCO 2 V A.
The depth and rate of ventilation with carbon dioxide acting as the primary stimulus for ventilation. Tap card to see definition. In normal circumstances our primary stimulus to breaths is PaCO 2.
What Is The Primary Stimulus For Breathing

Comments
Post a Comment